How fast is 5G?
Users of 5G devices in four countries – the US, Australia, Switzerland and South Korea – can already experience maximum download speeds of over 1 Gbps, according to the latest survey of crowdsourced data from OpenSignal. 5g speeds
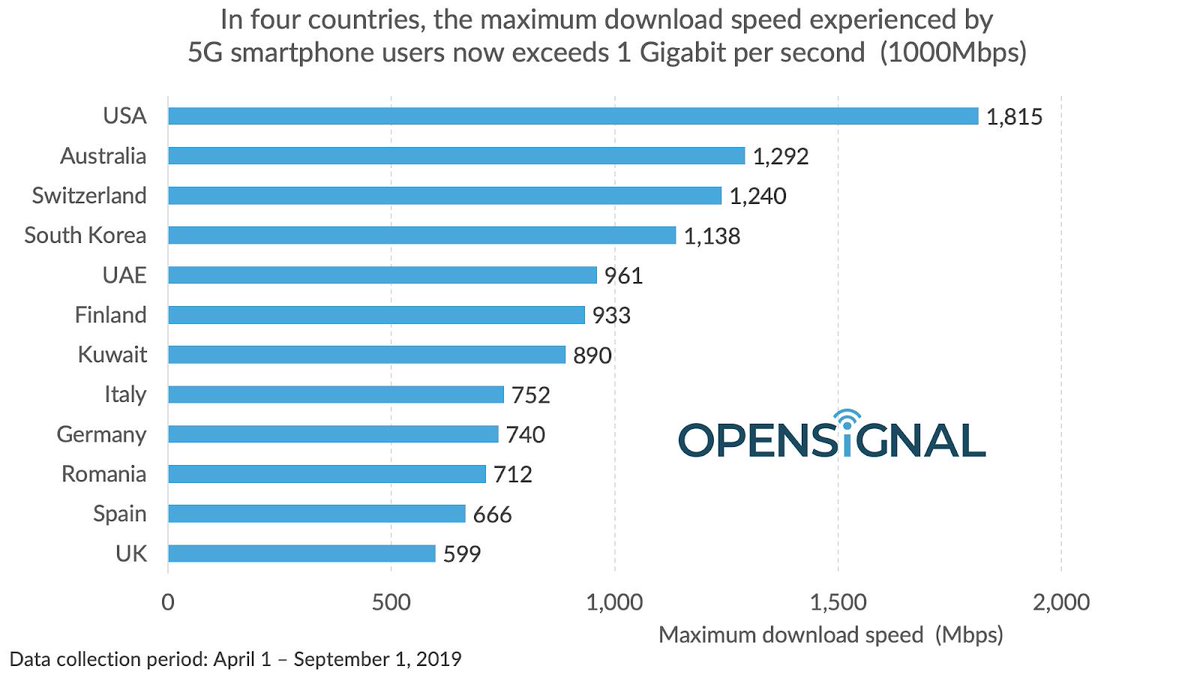
In most countries, the maximum speed experienced by 5G smartphone users has increased in the two months since OpenSIgnal last ran this analysis. Of the eight countries they analyzed in July, only the U.S. has seen no increase in the maximum download speed, likely because these are already so fast. But in the U.K., Switzerland and South Korea the increase in maximum speed is under 10%.
Opensignal has included a number of new 5G countries this time. Germany jumps over Spain and the U.K., despite its later 5 G service launch, with a maximum speed of 740 Mbps, as do both Romania with 712 Mbps and Finland with an impressive 933 Mbps. 5g speeds
What are the differences between the previous generations of mobile networks and 5 G?
A: The previous generations of mobile networks are 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G.
First generation – 1G
1980s: 1G delivered analog voice.
Second generation – 2G
Early 1990s: 2G introduced digital voice (e.g. CDMA– Code Division Multiple Access).
Third generation – 3G
Early 2000s: 3G brought mobile data (e.g. CDMA2000).
Fourth generation – 4G LTE
2010s: 4G LTE ushered in the era of mobile broadband.
1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G all led to 5 Gen., which is designed to provide more connectivity than was ever available before.
5 G is a unified, more capable air interface. It has been designed with an extended capacity to enable next-generation user experiences, empower new deployment models and deliver new services.
With high speeds, superior reliability and negligible latency, 5 G will expand the mobile ecosystem into new realms. 5 gen. will impact every industry, making safer transportation, remote healthcare, precision agriculture, digitized logistics — and more — a reality.









