Google’s Cloud Text-to-Speech gets more languages and voices
Google Cloud Text-to-Speech is intended to help companies develop better conversational interfaces for the services they supply. It works by transforming written text into artificial speech that’s spoken in realistic human voices.
With the service, Google is targeting three main markets: voice response systems for call centers; “internet of things” products such as car infotainment systems, TVs and robots; and applications such as podcasts and audiobooks, which convert text into speech.
In a blog post, Google product manager Dan Aharon said Cloud Text-to-Speech is getting 12 new languages or variants, including Czech, English (India), Filipino, Finnish, Greek, Hindi, Hungarian, Indonesian, Mandarin Chinese (China), Modern Standard Arabic and Vietnamese. The update means Cloud Text-to-Speech is now available in a total of 33 languages and variants.
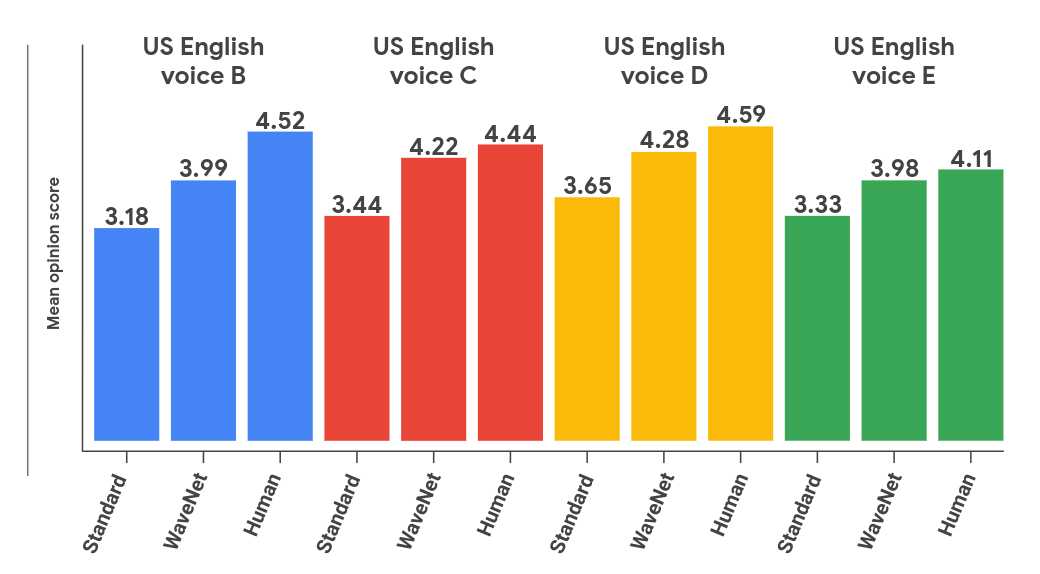
The service is also getting a whopping 76 new voices, bringing the total available to 187. Of these, 38 are powered by Google’s WaveNet service, which is a deep neural network for generating raw audio that’s said to generate more realistic-sounding voices. So there are now 95 WaveNet voices in total, with at least one for each of the 33 supported languages and variants.
Google says its WaveNet voices are important because people who call contact centers or use verbal commands to speak to devices expect a voice that sounds both natural and human. WaveNet does this better than any other technology available, closing the “perceived quality gap” between speech synthesis and human speech in U.S. English by 70% per Mean Opinion Score, Aharon said.
“The practical impact is that for most listeners, a WaveNet voice makes human/computer interaction a smooth and familiar experience,” Aharon said. “With these updates, Cloud Text-to-Speech developers can now reach millions more people across numerous countries with their applications — with many more languages to come.”
Constellation Research Inc. analyst Holger Mueller said the updates to Cloud Text-to-Speech were significant, even though at first glance it just appears to be “more languages and voices.” Most importantly, it shows that Google is putting its machine learning architecture to good use, he said.
Here are some key features:
- Variety of Voices: Google Cloud offers multiple voice options, including different accents and genders, allowing for more personalized and diverse auditory experiences.
- Customization: Users can customize speech parameters, such as pitch, speaking rate, and volume gain, to better suit their needs.
- SSML Support: The service supports Speech Synthesis Markup Language (SSML), which allows users to enhance speech with effects like emphasis, pauses, and pronunciation adjustments.
- Real-Time Streaming: Google Cloud Text-to-Speech can provide real-time streaming, making it suitable for interactive applications, such as chatbots and virtual assistants.
- Use Cases: It’s commonly used in various applications, including accessibility tools, voice assistants, educational software, and media production.
- API Integration: The service can be easily integrated into applications via its REST API, allowing developers to implement text-to-speech functionality into their software solutions.