eSIM vs iSIM
The iSIM technology is set to replace the traditional SIM cards and eSIM. While most people still use traditional SIM cards, the iSIM is expected to revolutionize the smartphone industry.
A SIM card, either eSIM or iSIM, is what makes your phone work, allowing it to send and receive data, make calls and send texts. Without one, your phone would be effectively useless as a phone.
What is a SIM?
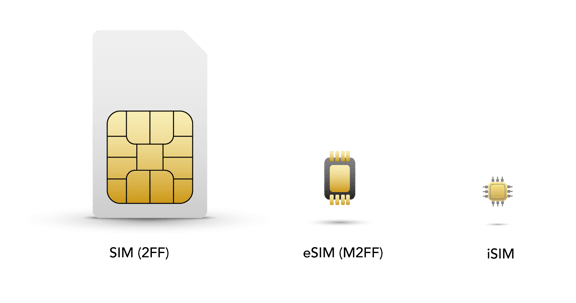
A SIM is a Subscriber Identity Module. It’s a software component that associates a device with a specific subscriber and identifies the device type to the cellular network, among other things. The SIM stores information such as an International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI), International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI), and operator profile. SIM cards require a slot in the device. They’re removable, which allows someone to reuse their SIM card in another device or install a new card to access different networks
What is an eSIM?
An eSIM is an Embedded Subscriber Identity Module. The eSIM standard was first released in 2016, and as SIM card manufacturers raced to offer the latest technology, some ambiguity developed around what “eSIM” actually referred to. Technically, an Embedded Subscriber Identity Module is a specific SIM form factor.
The MFF2 was the first form factor that could be soldered directly onto a cellular device’s circuit board. But eSIMs also came with an advanced new capability: they can switch carriers Over-the-Air (OTA).
What is an iSIM?
An iSIM is an Integrated Subscriber Identity Module. It’s essentially a more advanced eSIM. It provides the same functionality, but you don’t have to solder it onto the device’s circuit board. Instead, an iSIM has a dedicated space on the System of Chip (SoC), where it’s protected by a Tamper Resistant Element (TRE).
Integrated SIMs continue the tradition of making cellular components smaller and more efficient, and it’s just a fraction of the size of an MFF2 (eSIM), which was already substantially smaller than a traditional SIM card.
Qualcomm, in partnership with Thales Group, has developed the iSIM, which is built into the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 CPU, eliminating the need for SIM trays and tools. The iSIM will be fully compliant with the GSMA remote SIM provisioning standard and will be remotely managed, similar to the eSIM.
Did you know the Qualcomm Kryo CPU in the @Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 delivers 35% faster performance and 40% better power efficiency? Learn more about our our newest premium mobile platform: https://t.co/HKAxEHRAyp
— Qualcomm (@Qualcomm) March 3, 2023
Who Can Get iSIM on Phone Now? eSIM vs iSIM
As of right now, the ONLY phones that will be able to run iSIM are those that use Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 CPU.
Qualcomm’s chip is the first to have its iSIM technology officially certified by the GSMA.
Announced at MWC 2023, Qualcomm confirmed the new iSIM will be fully compliant with the GSMA remote SIM provisioning standard.
What this means is simple: the subscriptions – your data plan and everything that comes with it – are remotely managed, like eSIM. For those that have been paying attention, you’ll remember that Vodafone, Qualcomm and Thales successfully demonstrated a smartphone that utilizes iSIM back in 2022. eSIM vs iSIM
With the advent of phones running on Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Gen 2, iSIM is now ready to be deployed commercially inside phones, allowing consumers in the USA, UK, and Europe to ditch their physical SIM cards in favor of this new, fully integrated option.
eSIM vs iSIM: What’s The Difference?
eSIM
The eSIM, or embedded SIM, is a chip that can be programmed and is built into a smartphone. It performs the same functions as a physical SIM card and is not tied to any specific carrier, allowing for easy switching between networks.
To activate a new connection or change carriers, a user with an eSIM-compatible device simply needs to download and install a configuration file, often provided as a QR code by mobile networks.
The ultimate goal of eSIM technology is to replace physical SIM cards altogether in smartphones and other devices.
In fact, the Apple iPhone 14 series in the US was launched exclusively with eSIM, which has spurred other smartphone manufacturers to consider adopting eSIM technology as the only option for their devices.
iSIM
An iSIM, or integrated SIM, is a type of SIM technology that embeds the SIM functionality directly into the device’s processor.
This means that devices with iSIM will not require a physical SIM card and will be able to connect to different mobile networks using software rather than hardware.
iSIM offers enhanced security features and more space for additional applications compared to traditional SIM cards or eSIM.
It is believed that in the future, providing carriers and networks get onboard, iSIM will become the default method of managing phone users’ subscriptions in the next few years.
iSIM Benefits vs eSIM
Beyond things like reducing waste, as you’ll no longer require a plastic SIM card, iSIM comes with a range of additional benefits.
The main takeaways are pretty clearcut:
- iSIM requires far less space than eSIM;
- iSIM is more secure because it is directly integrated with the SoC, so it cannot be removed or tampered with;
- iSIM also comes with a Secure Processing Unit which adds an additional layer of protection;
- And, finally, iSIM does not require any power like eSIM and SIM cards.
Let us compare iSIM and eSIM using a table:
| Feature | eSIM | iSIM |
| Physical form | An unremovable chip is soldered to the motherboard of the device. | Integrated into the SoC |
| Space | Removes the need for a physical SIM card slot, thereby saving lots of space in the device. | It saves even more space by removing the need for a chip in the motherboard for SIM. |
| Security | More secure than a physical SIM card as it’s embedded in the device. | More secure and tamper-resistant than eSIM. |
| Carrier Provisioning | Carrier profiles can be downloaded and installed by the user or carrier. | Similar to eSIM. |